Clustering¶
Example of how to cluster a set of points. The points are randomly drawn from three different distributions. The clustering algorithm will attempt to dermine which points belong to the same set.
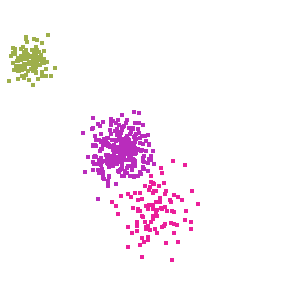
Output from example. Each cluster has its own color and each point is colorized to show the cluster it belongs to.¶
1// if true it will create the clusters from a gaussian distribution.
2// Otherwise an uniform distribution is used.
3public static boolean gaussian = true;
4public static Random rand = new Random(324);
5public static boolean clicked = false;
6
7public static void main( String[] args ) {
8 int dof = 2; // degree of freedom of the 2D point
9 var points = new ArrayList<double[]>();
10
11 // Accessor is used instead of a list directly because it becomes more efficient in very large datasets
12 var accessor = new ListAccessor<>(points,
13 ( src, dst ) -> System.arraycopy(src, 0, dst, 0, dof), double[].class);
14
15 // create 3 clusters drawn from a uniform square distribution
16 points.addAll(createCluster(5, 7, 2, 100));
17 points.addAll(createCluster(1, 2, 1, 120));
18 points.addAll(createCluster(4, 5, 1.5, 300));
19
20 // remove any structure from the point's ordering
21 Collections.shuffle(points);
22
23 ComputeClusters<double[]> cluster = FactoryClustering.kMeans(null, dof, double[].class);
24 ComputeClusters<double[]> cluster = FactoryClustering.gaussianMixtureModelEM_F64(1000, 500, 1e-8, dof);
25
26 cluster.initialize(rand.nextLong());
27
28 // visualization stuff
29 var gui = new Gui(points);
30
31 var frame = new JFrame();
32 frame.add(gui, BorderLayout.CENTER);
33 frame.pack();
34 frame.setVisible(true);
35 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
36
37 // Run the cluster algorithm again each time the user clicks the window
38 // This allows you to see how stable the clusters are
39 while (true) {
40 int numClusters = 3;
41 cluster.process(accessor, numClusters);
42
43 AssignCluster<double[]> assignment = cluster.getAssignment();
44 gui.update(assignment);
45
46 while (!clicked) {
47 Thread.yield();
48 }
49 clicked = false;
50 }
51}
52
53public static List<double[]> createCluster( double x, double y, double width, int N ) {
54
55 List<double[]> points = new ArrayList<>();
56
57 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
58 double[] p = new double[2];
59
60 if (gaussian) {
61 p[0] = rand.nextGaussian()*width/3 + x;
62 p[1] = rand.nextGaussian()*width/3 + y;
63 } else {
64 p[0] = rand.nextDouble()*width - width/2 + x;
65 p[1] = rand.nextDouble()*width - width/2 + y;
66 }
67
68 points.add(p);
69 }
70
71 return points;
72}
73
74/**
75 * Basic visualization which draws the points in a window. Each color is assigned a different random color
76 */
77public static class Gui extends JPanel implements MouseListener {
78 AssignCluster<double[]> assignment;
79 List<double[]> points;
80 Color[] colors;
81
82 public Gui( List<double[]> points ) {
83
84 this.points = points;
85
86 setPreferredSize(new Dimension(300, 300));
87 setBackground(Color.WHITE);
88
89 addMouseListener(this);
90 }
91
92 public synchronized void update( AssignCluster<double[]> assignment ) {
93 this.assignment = assignment;
94 colors = new Color[assignment.getNumberOfClusters()];
95 for (int i = 0; i < colors.length; i++) {
96 colors[i] = new Color(rand.nextInt() | 0x080808);
97 }
98 repaint();
99 }
100
101 @Override
102 public synchronized void paintComponent( Graphics g ) {
103 if (assignment == null)
104 return;
105
106 super.paintComponent(g);
107
108 Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D)g;
109
110 double scaleX = getWidth()/10.0;
111 double scaleY = getHeight()/10.0;
112
113 for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) {
114 double[] p = points.get(i);
115 int x = (int)(p[0]*scaleX + 0.5);
116 int y = (int)(p[1]*scaleY + 0.5);
117
118 g2.setColor(colors[assignment.assign(p)]);
119 g2.fillOval(x - 2, y - 2, 5, 5);
120 }
121 }
122
123 @Override
124 public void mouseClicked( MouseEvent e ) {
125 clicked = true;
126 }
127
128 @Override
129 public void mousePressed( MouseEvent e ) {
130 }
131
132 @Override
133 public void mouseReleased( MouseEvent e ) {
134 }
135
136 @Override
137 public void mouseEntered( MouseEvent e ) {
138 }
139
140 @Override
141 public void mouseExited( MouseEvent e ) {
142 }
143}